GS1 Standards
GS1 is a global organization that develops and maintains standards for business communication, focusing on supply chain management and product identification. The most well-known of these standards is the barcode, which encodes product information in a machine-readable format. GS1 barcodes are ubiquitous, facilitating the seamless movement of goods across industries and borders by ensuring consistent identification of products, assets, and services. This global standardization enables efficient inventory management, reduces errors, and improves traceability, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
MapleJet offers cutting-edge solutions for businesses adhering to GS1 standards, providing reliable tools for precise barcode marking. Our advanced technologies are designed to meet GS1 barcode standards, ensuring that every product label is accurate, scannable, and compliant with global regulations.
GS1 Standards have been in use since 1973, when the grocery industry unified its approach to business by adopting the U.P.C. barcode, enhancing speed and efficiency at retail checkouts. Forty-five (45) years later, this U.P.C. barcode is still used at check-out counters. Various GS1 standards have been introduced, throughout the years, and adopted by numerous industries, including Food, Beverage, and Pharmaceutical.
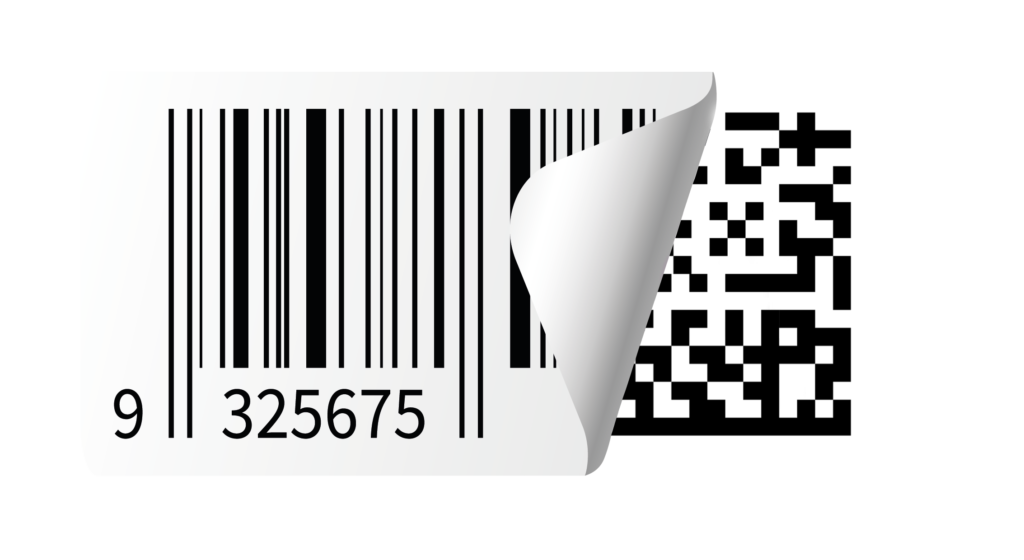

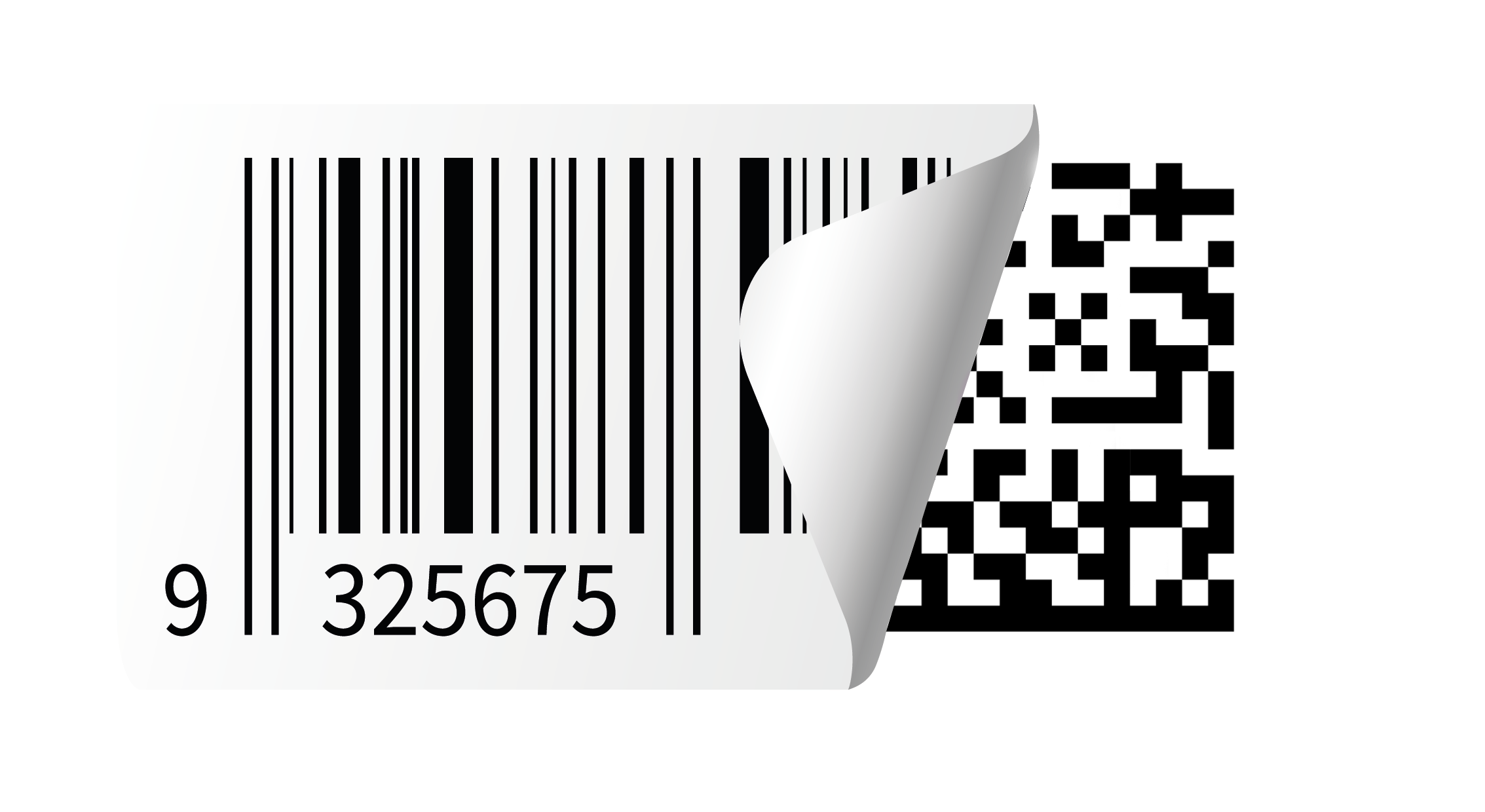
Figure 1. GS1.org is replacing UPC and EAN Code with QR and Data Matrix Code with Sunrise 2027
In 2027, GS1 is officially launching GS1 Sunrise 2027. This campaign encourages various organizations to move towards more dense 2D Barcodes (2D Data Matrix or QR codes) that can store more information, including additional and dynamic data such as lot numbers, production or expiry dates, URLs, location data, nutritional information, and more.
Benefits of GS1 Tracking
For Consumers: GS1 tracking guarantees product authenticity and safety. By scanning a barcode, consumers can access detailed product information, verify its origin, and ensure it meets regulatory standards. This transparency fosters trust and empowers informed purchasing decisions.
For Businesses: GS1 tracking enhances operational efficiency and supply chain visibility. Accurate tracking systems allow companies to manage inventory effectively, reduce waste, and respond swiftly to recalls or quality issues. It also supports compliance with industry regulations and facilitates international trade by standardizing product identification across markets.
Whether you’re printing 2D barcodes, such as DataMatrix or QR codes, our systems deliver exceptional clarity on a variety of surfaces, including packaging materials, bottles, and cases. MapleJet’s innovative printers are built to handle high-speed production environments, meeting the demands of industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and logistics.
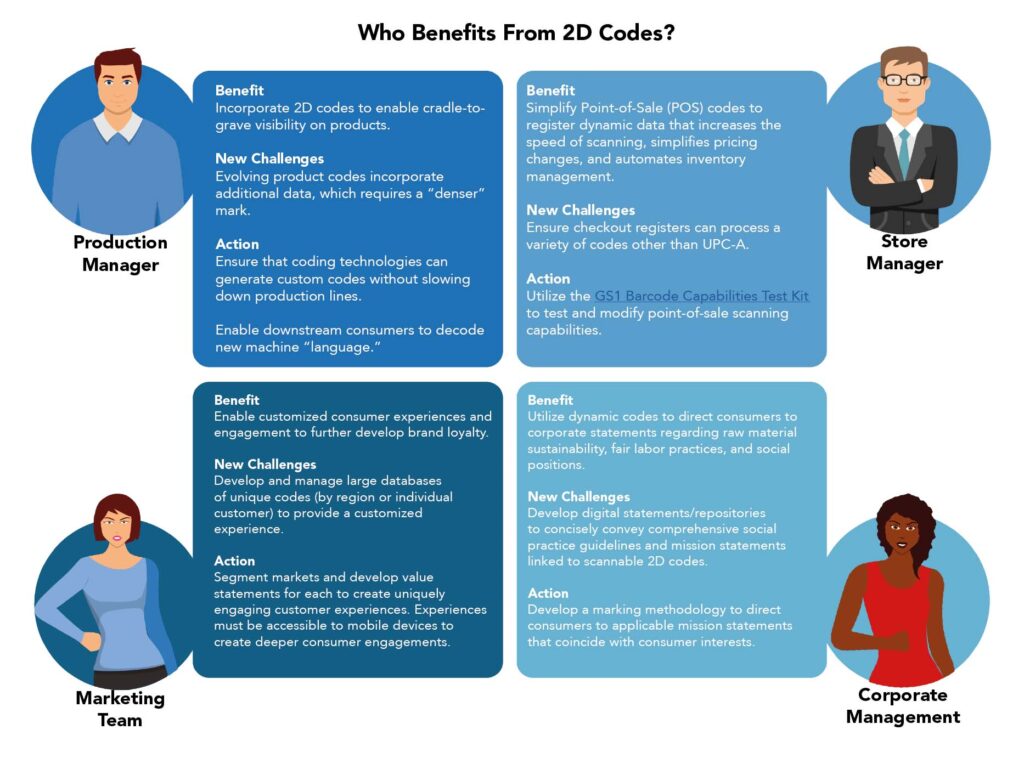
Figure 2. Figure 2. “Who Benefits From 2d Codes” retrieved from White Paper: Evolution of Coding and Marking by MapleJet & Funai
Businesses Embracing GS1 2D Barcode Printing Ahead of GS1 Sunrise 2027
This is an excerpt from Evolution of Product Coding [White Paper].
“To address rapidly changing coding requirements, GS1.org, the leading authority on coding standards, has unveiled the “Sunrise 2027” plan, which aims to phase out the UPC code by 2027. The adoption of 2D barcodes offers a standardized approach to fulfilling both supply chain demands and evolving consumer needs.
Several major companies have joined pilot programs, each with distinct objectives. These companies and their goals include:
Woolworths (Woolies): Forecasting, inventory management, and overall efficiency”
Walmart: Supply chain management
Procter & Gamble: Use of GS1 Digital Link for smart packaging and increasing consumer engagement
Pepsi: QR codes for lottery and cash prizes as part of their UEFA Champions League sponsorship in the UK
Challenges in Printing 2D Barcodes with Coding Technology
The challenges of printing 2D barcodes using various technologies primarily revolve around print quality, speed, and data entry.
1. Print Quality: Ensuring the print quality of 2D barcodes is crucial for both human readability and machine scanability. This necessitates high-resolution printing to achieve the precise dot density required for accurate scanning. Technologies must be capable of producing barcodes with sufficient clarity and contrast to maintain data integrity across various scanning environments.
2. Printing Speed: High-speed printing is a significant requirement for large-scale production environments. Technologies like Continuous Inkjet (CIJ) offer rapid throughput but often face limitations in print resolution, particularly for dense data encoding such as 2D Barcode printing. The challenge lies in achieving a balance between high-speed operation and maintaining the resolution necessary for accurate 2D barcode printing.
3. Data Entry and Integration: Printing 2D barcodes involves embedding complex data sets, including URLs, batch numbers, and additional data. The integration of this data into the barcode must be seamless to avoid errors and ensure efficient data handling. Effective data management platform and barcode-designing tools are essential to streamline this process and ensure that all required information is accurately encoded.
Advantages of MapleJet Coding and Marking Printer for Printing GS1 2D Barcodes
MapleJet is always at the forefront of developing innovative, future-proof technology. The design incorporated into its technology strongly supports the implementation of GS1 Sunrise 2027. MapleJet’s series of Hx Thermal Inkjet Printers stands out with the following capabilities:
- High-Speed Printing: The current printing speed of MapleJet Hx TIJ printers can reach up to 120 meters per minute at 160 dpi, which offers a significantly higher resolution compared to CIJ printers which offer a maximum of 80 dpi. Although CIJ can double the speed of TIJ printers, printing 2D codes at less than 80 dpi can make the codes unscannable. Many high-speed applications that rely on CIJ for printing production dates might face challenges when incorporating the production date and expiry into QR or Data Matrix codes.
- High-Resolution Printing: With the capability to print up to 600 dpi, MapleJet Hx TIJ printers ensure that the denser data encoded into 2D barcodes remain scannable at supermarkets and point-of-sale stations. This high-resolution printing is crucial for both tracking purposes and maintaining brand aesthetics.
- User-friendly Barcode Designing Tool: The MapleJet Hx printer is equipped with the Hx Manager software, a unified platform accessible via any smart device (iOS, Android, Windows, etc.). Hx Manager is a user-friendly application where operators can design various types of barcodes required in their production line.
Additional Key Features of MapleJet’s Hx TIJ Printers:
- MapleJet Cloud: MapleJet Cloud provides centralized control over multiple printing stations. This allows for uniformity in barcode quality and standards across various production sites, simplifying quality assurance and compliance with GS1 standards.
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: Operators can design and control print messages via smartphones, eliminating the need for dedicated controllers and promoting operational flexibility.
- Maintenance-Free Technology: The Hx Nitro series requires minimal maintenance, with no need for regular field engineer visits. Cartridge replacement is straightforward, making the printer as good as new and reducing downtime.
- Field Upgrade: Remote updates ensure that the printers are always running the latest software without additional costs. Field upgrades allow for future infield software upgrades, making the hardware lifecycle longer than that of average printers in the market.
- Economy Mode: This feature reduces ink consumption by up to 50%, providing cost savings and increasing the number of prints per cartridge.
MapleJet’s commitment to innovation and quality is evident in its Hx Nitro series. By integrating GS1 Data Link and offering high-speed, maintenance-free barcode printing, MapleJet provides a comprehensive solution for modern manufacturing needs. These advancements not only enhance traceability and efficiency but also help businesses reduce costs and improve operational flexibility.
With intuitive interfaces and robust hardware, our GS1 standards enhance operational efficiency while ensuring seamless integration into production lines. Rely on MapleJet for next-level printing solutions that elevate product traceability and streamline your operations.






Recent Comments